Venereology
18 Dec 2020The diagnosis and treatment of venereal diseases is called venerology. Venereal diseases are transmitted through sexual contact. Some of the common venereal diseases are Syphilis, Gonorrhea, HIV Infection, Herpes Simplex and Genital Scabies, among others. Common venereal infections include Hepatitis B, Lymph Granuloma and Granuloma Inquinate. These diseases are transmitted by semen, vaginal secretions or blood during sexual intercourse. These are caused by micro-organisms that survive on the skin and the mucous membrane and can include viruses, bacteria, parasites and fungi.
Venerology drives it name from the Greek goddess Venus. She is associated with beauty, love and fertility. In the past venereal diseases were called the most formidable enemy of mankind. Though the advent of antibiotics has made the treatment of most diseases easy, in India, they continue to be a challenge due to social prejudice. Diseases like syphilis were unknown in India till the early 16th century, it was called “firangi roga”. In the second half of the 19th century, among British soldiers in India, it was the second most important reason for hospitalization. Similarly, AIDS, which most people thought was a Western disease, started spreading rapidly in India in the 1980’s.
Types of sexually transmitted disease
Syphilis
It is caused by bacteria and generally does not cause much discomfort to patients in the initial stages. It starts with the appearance of a round sore called chancre which can develop on the mouth, anus or genitals. If undetected, late stage syphilis can cause loss of vision, hearing, memory, heart diseases, brain/spinal cord infections and finally death. Syphilis can be easily treated with antibiotics though it can be fatal in newborn babies. It can be easily treated if detected early.
Chlamydia
Common symptoms include lower pain in the lower abdomen, discharge from penis/vagina and pain during sex/urination. If not treated the disease can cause infertility, infection in urethra/testicles/prostate gland and pelvic inflammatory disease. Antibiotics can help treat this disease easily.
Gonorrhea
Frequent urination, genital itching, sore throat, discharge from vagina/penis are common symptoms. It can lead to infection of the urethra, prostate and testicles, infertility, and pelvic inflammatory disease, if left untreated. Antibiotics are useful in treating this disease.
Cause: Virus
HIV
It damages the immune system and if left untreated leads to Stage 3 HIV or AIDS. Initially the patient suffers from cold, chills, fever, aches, sore throat, headache, nausea and rashes, pretty much like a flu. All these clear after a month. These may clear after a month or the patient may show persistent symptoms such as recurring fever, fatigue, headache and stomach related issues. Early and effective treatment options are available to manage this STI. Taking treatment early also reduces transmission risk.
HPV or Human Papilloma virus
This is commonly spread by intimate skin-to-skin contact and contact during sexual intercourse. It can be caused by different strains of virus. Common symptoms include warts on genitals, mouth and throat. Certain strains of the virus cause oral, cervical, vulvar, penile and rectal cancer. While there is no cure, there are vaccines that can protect again virus causing cervical cancer.
Herpes
It is caused by the Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV 1 and 2). There are two strains of the virus. HSV 1 causes oral herpes and cold cores. During oral sex it is passed from mouth to genitals causing genital herpes.
In the case of HSV 2, there are blistery sores around the genitals and in the case or oral herpes, sores are seen in and around the mouth. Pregnant women can pass this infection to their newborn which is called congenital herpes. While there is no cure for herpes, medication should be taken to prevent outbreaks and for pain alleviation.
Cause: Parasites
Trichomoniasis
It is caused by a tiny protozoan organism. It is passed from person to the other through genital contact. Symptoms include discharge from vagina and penis, burning sensation and itching in the genitals, pain during sex and urination, and frequent urination. Left untreated, it can cause infection of the urethra, pelvic inflammation and infertility.
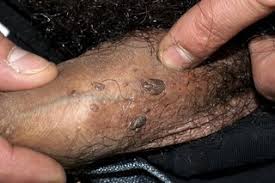
Pubic Lice
Common symptoms include genital itching, pink/red bumps in and around the genitals, low grade fever, lack of energy and irritability. Lice are found in pubic hair. Topical treatments can eliminate pubic lice. It can be prevented by minimizing skin to skin contact and not sharing bedding, towels and clothes.
Resurgence of the diseases in the last decade in India
The use of the term venereal disease has been increasingly replaced by the use of the term sexually transmitted diseases (STD) and more recently the term sexually transmitted infections (STI). STD’s include diseases that are caused by sexual intercourse and affect the genitalia. STI’s include infections affect the genitals/other parts of the body and are transmitted by sexual intercourse such as Hepatitis B or HIV.
Bacterial STD’s such as Chancroid and Gonorrhea are showing a decreasing trend whereas viral STD’s such as Herpes Genitals and Condyloma Acuminata are showing an upward trend. This decreasing trend has been due to a syndromic approach to tacking these diseases, treatability of bacterial infections, antibiotics and behavioral changes.
The spread of HIV due to unprotected sex among high risk partners and drug abuse is a matter of concern in India. We are also seeing an increase in syphilis among same sex partners. There is also an increase in STI’s, almost like an epidemic, due to liberal sexual mores among people including premarital sex and high risk sexual behavior.
Essence of early intervention and treatment
Transmission of STI’s can be prevented by early diagnosis and treatment. The quality of life of the infected person can also be improved by early clinical intervention. Patients with STI have a higher risk of acquiring or transmitting HIV infection through high risk behavior. Early treatment, counseling to ensure behavioral change and easy access to testing are necessary for preventing and managing STI’s. Most STI’s promote increased shedding of HIV. Untreated STI’s can cause infertility, HIV, cervical cancer, and pregnancy complications among others. HIV testing, counseling people exhibiting high risk sexual behavior and screening/testing of people with STI are some ways of breaking the transmission.